Difference between revisions of "UKCA Chemistry and Aerosol vn10.9 Tutorial 1"
| Line 113: | Line 113: | ||
==Checklist== |
==Checklist== |
||
| − | : <span style="font-size:21px">☐</span> |
+ | : <span style="font-size:21px">☐</span> List suites using <code>rosie go</code> |
| + | : <span style="font-size:21px">☐</span> Copy suites using the right-click menu |
||
| + | : <span style="font-size:21px">☐</span> Run suites using the play button |
||
Revision as of 17:29, 4 December 2017
UKCA Chemistry and Aerosol Tutorials at vn10.9+
Before starting these tutorials you should first make sure that you have completed the setup instructions. If you are using Linux or macOS you will only need to complete section 2.2 onwards.
Copying and Running an Existing Rose Suite
| Machine | UM Version/Configuration | Suite ID |
|---|---|---|
| ARCHER | vn10.9 N48L38 Intel Compiler | u-as101 |
| vm | vn10.9 N48L38 GNU Compiler | u-as159 |
If you are using PUMA & ARCHER, you will need to login to PUMA, e.g.
ssh -Y username@puma.nerc.ac.uk
If you are using the Met Office Virtual Machine, you will need to login to the VM, e.g.
vagrant ssh
You should then be asked for your SRS password.
Then launch the UM graphical user interface by:
rosie go
This should then load up a blank interface. Go to Edit Data source and select u. The go to the search panel and search for the correct base suite. This will then show all the suites that have this suite-id in it's history or title. You should just select the correctly named suite and not any of the others.
Right-click on the suite and click copy suite. A new box will open asking for the project - it is fine to press Forward here. On the next panel, it's fine to just press OK again as well.
The suite will now copy and checkout to your /home/$USER/roses directory, and will also appear when running rosie go.
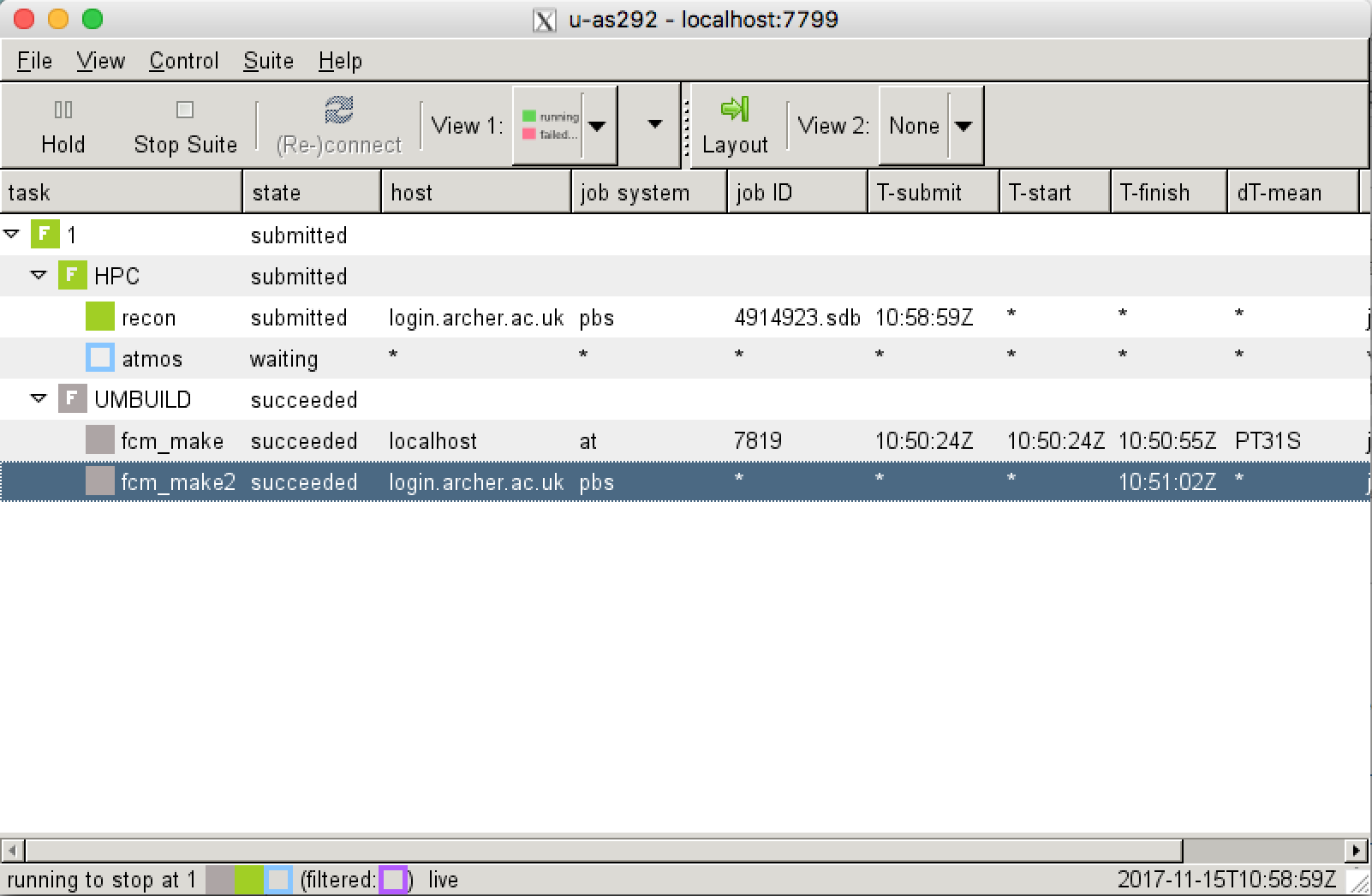
You should now right-click edit (or double-click) on this new suite, and click run, which is symbolised by a play symbol (i.e., a large grey arrow-head pointing to the right).
If you are using PUMA/ARCHER, this suite has been configured to manually compile, so you should follow the instructions on how to do that, to be sure that you can compile your suite as quickly as possible. It will take about 7 minutes to compile the code (fcm_make and fcm_make2 tasks), followed by about 3 minutes to run the reconfiguration step (recon), and then 1 minute to run the UM itself (atmos).
If you are using the VM, times will vary depending on the specifications of the host. It could take about 10 minutes to compile the code (fcm_make) for the first time (and about 1-2 minutes when recompiling), followed by about 1 minute to run the reconfiguration step (recon), and then about 12 minutes to run the UM itself (atmos).
When the suite has finished successfully it will then become blank with the message stopped with 'succeeded' in the bottom-left corner.
Version Control
Rose suites are all held under version control, using fcm. When making changes to a suite, you will need to save it before you can run the suite. Once you are happy with the settings, you can also commit these changes back to the repository - to do this change directory to the
/home/$USER/roses/[SUITE-ID]
and then type
fcm commit
a text editor will then open, and you should type a short message describing what the changes you have made do. You should then close the editor and type y in the terminal. It is recommended that you commit frequently (even on configurations that aren't working) as this protects you against mistakes and accidental deletions etc.
These suites can be viewed on the SRS here: https://code.metoffice.gov.uk/trac/roses-u (password required)
It is recommended that you commit your suites regularly.
Output Directory Structure
The output directory structure of rose suites are rather complex:
- You can find the latest & full job.out files in
- ARCHER:
/home/n02/n02/$USER/cylc-run/[SUITE-ID]/log/job/1/[JOB NAME]/NN- e.g. /home/n02/n02/luke/cylc-run/u-as292/log/job/1/atmos/NN
- These are also mirrored to PUMA, in your
/home/$USER/cylc-run/[SUITE-ID]directory.
- vm:
/home/vagrant/cylc-run/[SUITE-ID]/log/job/1/[JOB NAME]/NN- e.g. /home/vagrant/cylc-run/u-as297/log/job/1/atmos/NN
- This file contains what the UM writes out using the
umPrintsubroutine. These can also be viewed through the Gcylc GUI right-click menu from each step.
- Output from the individual processors (which are updated as the job is running can be found in
- ARCHER:
/work/n02/n02/$USER/cylc-run/[SUITE-ID]/work/1/[JOB NAME]/pe_output- e.g. /work/n02/n02/luke/cylc-run/u-as292/work/1/atmos/pe_output
- vm: /home/vagrant/cylc-run/[SUITE-ID]/work/1/[JOB NAME]/pe_output
- e.g. /home/vagrant/cylc-run/u-as297/work/1/atmos/pe_output
- A handy command to check the progress of the job is
- ARCHER:
tail -1000f atmos.fort6.pe00 | grep Atm_Step - vm:
tail -1000f atmos.fort6.pe0 | grep Atm_Step
- ARCHER:
- Output files in 64-bit fieldsfile format can be found in:
- ARCHER:
/work/n02/n02/$USER/cylc-run/[SUITE-ID]/work/1/atmos- e.g. /work/n02/n02/luke/cylc-run/u-as292/work/1/atmos
- Note: other suites may put the output into a different location, e.g.
/work/n02/n02/$USER/cylc-run/[SUITE-ID]/share/data/History_Data, and there are also post-processing settings that can be used to copy data to the RDF or JASMIN as the suite runs.
- vm: /home/vagrant/cylc-run/[SUITE-ID]/work/1/atmos/pe_output
- e.g. /home/vagrant/cylc-run/u-as297/work/1/atmos/pe_output
- Files can have various naming conventions. For these suites, they will be atmosa.pa19810901_00, but more generally they are likely to be of the form
[SHORT SUITE-ID]a.p[abcdefghijkmsyx]YYYYMMDD- e.g.
ag308a.pk19880901
- e.g.
[SHORT SUITE-ID]a.p[abcdefghijkmsyx]YYYYmon- e.g. ak468a.pe1989oct
Whilst this suite is running, take a look at Tutorial 2: Exploring Rose.
Viewing Output
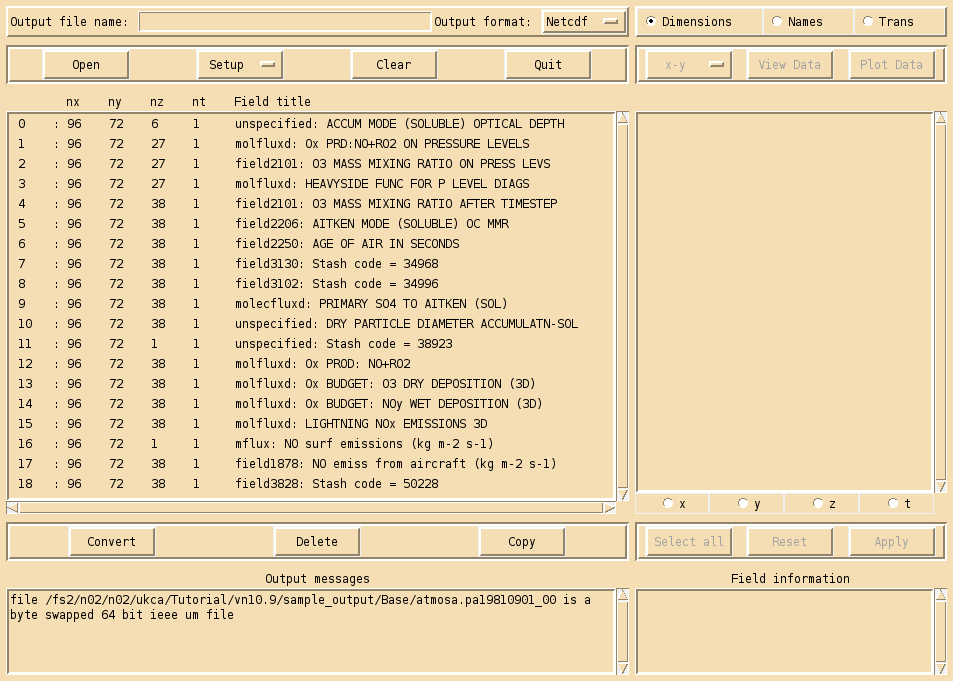
For more detailed plotting, tools such as the Iris and cf-python libraries can be used to view UM file formats directly. However, for quick viewing, Xconv is a very useful tool.
To view these files, do
xconv atmosa.pa19810901_00
As well as viewing files, you can use Xconv to convert these files to netCDF, by filling in the Output file name: box (e.g. foo.nc), and then clicking convert. If no path is defined, this will save the file in the same directory that you opened Xconv from.
Example output from the UKCA training suite can be found at /work/n02/n02/ukca/Tutorial/vn10.9/sample_output/Base/atmosa.pa19810901_00 on ARCHER.
Checklist
- ☐ List suites using
rosie go - ☐ Copy suites using the right-click menu
- ☐ Run suites using the play button
Written by Luke Abraham 2017