UKCA & UMUI Tutorial 3: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[UKCA & UMUI Tutorials | Back to UKCA & UMUI Tutorials]] |
[[UKCA & UMUI Tutorials | Back to UKCA & UMUI Tutorials]] |
||
=Running an existing UKCA job= |
|||
You will need to change a number of options within the UMUI to allow you to run this job successfully, such as your username, HECToR TIC code (if needed) etc. If you are using the MONSooN job you may also need to change the project group in |
You will need to change a number of options within the UMUI to allow you to run this job successfully, such as your username, HECToR TIC code (if needed) etc. If you are using the MONSooN job you may also need to change the project group in |
||
| Line 121: | Line 121: | ||
There are then three file extensions: '''.comp.leave''' for compilation output, '''.rcf.leave''' for reconfiguration output, and '''.leave''' for the model output. |
There are then three file extensions: '''.comp.leave''' for compilation output, '''.rcf.leave''' for reconfiguration output, and '''.leave''' for the model output. |
||
It is often easier to list your files in this directory by date, but using <tt>ls -ltr</tt>. |
|||
===Compilation Output (.comp.leave)=== |
===Compilation Output (.comp.leave)=== |
||
This gives the output from either the XLF compiler on MONSooN or the Cray compiler on HECToR. If the compilation step has an error and the code is not compiled you can find the source of the error by opening this file and searching for '''failed''' - this will highlight which routine(s) caused the problem. You may also get more detailed information such as the line number which had the error. In this case you can open the file on the supercomputer and view the line, as the line number given will not match with the line in your working directory on PUMA due to merging source code and the use of include files. Remember to make any required changes to your PUMA source code however! |
|||
===Reconfiguration Output (.rcf.leave)=== |
===Reconfiguration Output (.rcf.leave)=== |
||
This gives output from the reconfiguration step, if run. At older UM versions, such as UM7.3 this output was found in the model output .leave file. |
|||
===Model Output (.leave)=== |
===Model Output (.leave)=== |
||
This gives output from the code which is generated as it is running, although this file is only updated and closed when the job finishes. To view the output generated as it is running you will need to see the output in the <tt>pe_output/</tt> directory mentioned above. |
|||
To run efficiently the UM is split into many domains, which communicate with each other with parallel calls, during runtime. The exact decomposition is defined in ''Model Selection → User Information and Submit Method → Job submission method'', in the number of processes East-West and North South boxes. If you have a 16x16 decomposition there will be 256 processes, running on 256 cores of the supercomputer (4 nodes of MONSooN, |
|||
Revision as of 09:30, 11 June 2013
Running an existing UKCA job
You will need to change a number of options within the UMUI to allow you to run this job successfully, such as your username, HECToR TIC code (if needed) etc. If you are using the MONSooN job you may also need to change the project group in
Model Selection -> Post Processing -> Main Switch + General Questions
if you want to send output data to the /nerc data disk (this is advisable).
Once you have made these changes you can submit your job. First click Save, then Process, and once this has completed, click Submit. This will then extract the code from the FCM repositories and submit them to the supercomputer. If you are running on MONSooN you will need to enter your passcode at this stage.
Checking the progress of a running job
Log-in to the supercomputer, and check that your job is running. For HECToR do
qstat -u $USER
and for MONSooN do
llq -u $USER
This should give a list of your running jobs. For example, on MONSooN you should get something like
$ llq -u $USER Id Owner Submitted ST PRI Class Running On ------------------------ ---------- ----------- -- --- ------------ ----------- mon001.64641.0 nlabra 6/5 12:36 R 50 parallel c139 1 job step(s) in query, 0 waiting, 0 pending, 1 running, 0 held, 0 preempted
You can also check how far a job has gone while it is running. To do this you will need to cd into the job directory (this will be on your /work space on HECToR or your /projects space on MONSooN). When you do this, you will see something like this
$ ls baserepos/ pe_output/ umrecon/ xhklg.apstmp1 xhklg.astart xhklg.out xhklg.stash xhklg.xhist xhklga.pc19920901 bin/ umatmos/ umscripts/ xhklg.apsum1 xhklg.list xhklg.requests xhklg.umui.nl xhklga.da19920921_00 xhklga.pe1992sep
Now cd into the pe_output/ directory and do
$ tail -f jobid.fort6.pe0 | grep Atm_Step
Atm_Step: Timestep 1744 Model time: 1992-09-25 05:20:00
Atm_Step: Timestep 1745 Model time: 1992-09-25 05:40:00
Atm_Step: Timestep 1746 Model time: 1992-09-25 06:00:00
Atm_Step: Timestep 1747 Model time: 1992-09-25 06:20:00
Atm_Step: Timestep 1748 Model time: 1992-09-25 06:40:00
Atm_Step: Timestep 1749 Model time: 1992-09-25 07:00:00
(changing jobid as appropriate for your job).
Viewing and extracting output
To take a look at the output, you will need to change into the directory where the data has been archived. On HECToR this should be in the archive/ sub-directory, on MONSooN it will be on /nerc/project/$USER/jobid. Once in this directory ls to see the file listing
$ ls xhklga.pm1992sep.pp
As you can see, there is only one file present, the "pm" file. This file is a montly-mean file that has come from the climate-meaning stream (climate-meaning has been covered in more detail in the What is STASH? tutorial).
$ ls xhklga.pm1992sep.pp
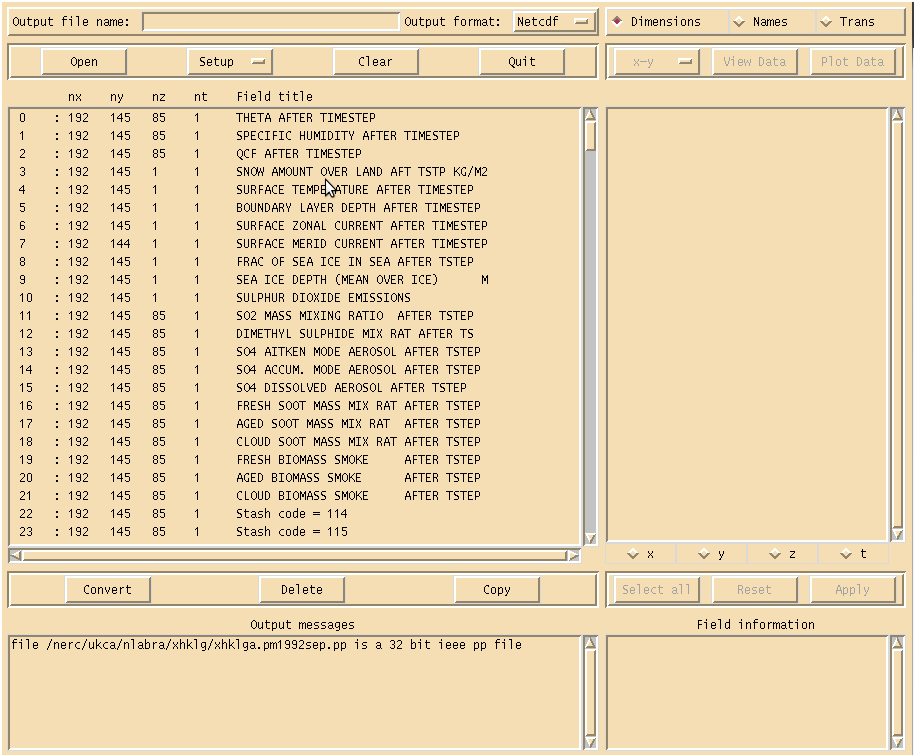
To quickly view output you can use Xconv, which provides a simple data viewer. It can also be used to convert the UM format output files to netCDF. You can open this file by
$ xconv -i xhklga.pm1992sep.pp
which will show the Xconv window as can been seen in Figure 1. If you scroll down the list of fields you will find ones that begin
Stash code = 34...
e.g. Stash code = 34001 etc. These are the UKCA chemical tracer and diagnostic fields (although they are not labeled as such by default). A full listing of these can be found in the listing of UKCA fields at UM8.2. More information has been given on STASH in the What is STASH? tutorial.
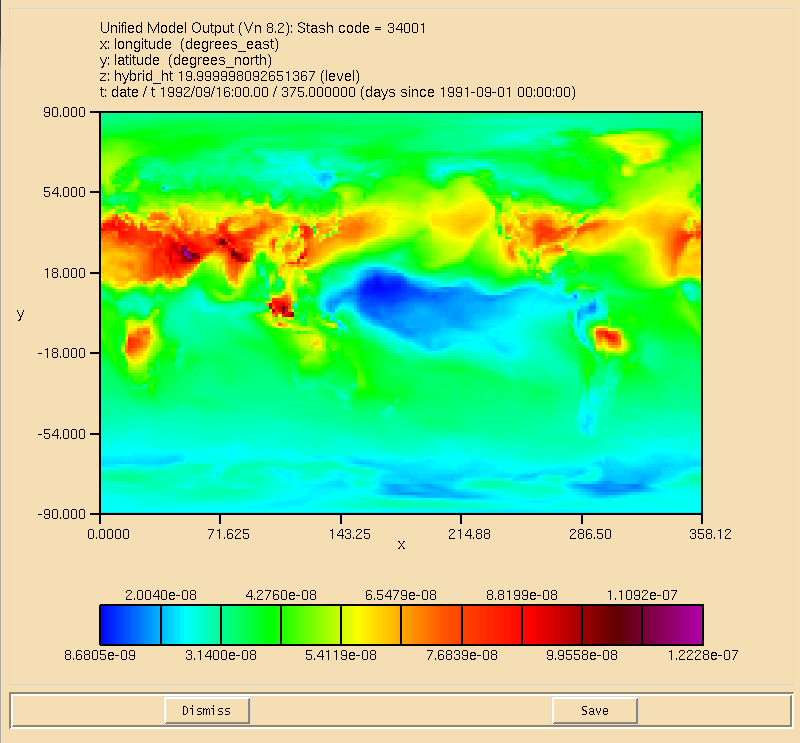
You can use Xconv to view certain fields. For example, you could view the surface ozone concentration double-clicking on the Stash code = 34001 field and clicking the Plot data button (see Figure 2). While this is good to quickly check data, the plotting functions are rather limited as it is not possible to change e.g. the colour-bar, the scale, add a map projection etc. It is advisable to either export fields as netCDF from within Xconv, or to use another program, such as IDL (using the Met Office library) or Python (using either cf-python or Iris) which is able to read the UM PP/FieldsFile format directly.
To export fields as netCDF select them using the mouse (they should then highlight blue), enter a name for the netCDF file in the Output file name box (making sure that the Output format is Netcdf) and click the Convert button. The window on the bottom right will show the progress of the conversion. For single fields this is usually quite quick, but it is possible to use Xconv to open multiple files containing a series of times. In this case Xconv will combine all the individual times into a single field, and outputting this can take some time.
One issue you may have is that Xconv uses a quantity called the field code to determine the variable name of each field (the netCDF name attribute). For UKCA tracer fields at UM8.2 this code is all the same, so all variables will be called field1861. It is possible to change the short field name in Xconv, prior to outputting a netCDF file. Select the variable you wish to output and select the Names button on the top-right of the Xconv window. Delete the contents of the short field name box and replace it with what you would like, e.g. for ozone (Stash code 34001) you may wish to use the CF standard name mass_fraction_of_ozone_in_air (as the units of UKCA tracers are kg(species)/kg(air)). The click apply and output the field as normal. When running ncdump on the resultant netCDF file you should see something like
float mass_fraction_of_ozone_in_air(t, hybrid_ht, latitude, longitude) ;
mass_fraction_of_ozone_in_air:source = "Unified Model Output (Vn 8.2):" ;
mass_fraction_of_ozone_in_air:name = "mass_fraction_of_ozone_in_air" ;
mass_fraction_of_ozone_in_air:title = "Stash code = 34001" ;
mass_fraction_of_ozone_in_air:date = "01/09/91" ;
mass_fraction_of_ozone_in_air:time = "00:00" ;
mass_fraction_of_ozone_in_air:long_name = "Stash code = 34001" ;
mass_fraction_of_ozone_in_air:units = " " ;
mass_fraction_of_ozone_in_air:missing_value = 2.e+20f ;
mass_fraction_of_ozone_in_air:_FillValue = 2.e+20f ;
mass_fraction_of_ozone_in_air:valid_min = 8.680486e-09f ;
mass_fraction_of_ozone_in_air:valid_max = 1.84475e-05f ;
Once you have your data as netCDF it is then possible to use any standard visualisation or processing package to view and manipulate the data.
.leave Files
The text output from any write statements within the code, or giving information about compilation, is outputted to several files with the extension .leave. These will either be placed in your $HOME/output directory on MONSooN or you $HOME/um/umui_out directory on HECToR.
You will have three .leave files, one for the compilation, one for the reconfiguration step (if run), and one for the UM itself. By default for climate runs these will all have a common format, starting with 4 blocks of letters and numbers, like this:
xhklg000.xhklg.d13156.t092342
where this breaks down to
| jobidXXX | e.g. xhklg000 | The jobid of the job, followed by the job-step number. For compilation and reconfiguration jobs, this will be 000, but as the CRUN progresses this number will increment by 1 for each step, and then cycle round back through 000 (if you run more than 999 steps). |
| jobid | e.g. xhklg | The jobid of the job as listed in the UMUI. |
| dXXXXX | e.g. 13156 | The year (the last two digits, i.e. 2013 is 13) and the day of the year as 3 digits (i.e. 001-366, so this file was created on the 5th June). |
| tXXXXXX | e.g. 092342 | The time in HHMMSS format, as recorded by the system clock on the supercomputer. |
Using this format this means that file was created on the 5th June 2013 at 09:23:42. Note that the timestamp on the file will be later than this, as this is the time the file was created, not the time that it was last written to.
There are then three file extensions: .comp.leave for compilation output, .rcf.leave for reconfiguration output, and .leave for the model output.
It is often easier to list your files in this directory by date, but using ls -ltr.
Compilation Output (.comp.leave)
This gives the output from either the XLF compiler on MONSooN or the Cray compiler on HECToR. If the compilation step has an error and the code is not compiled you can find the source of the error by opening this file and searching for failed - this will highlight which routine(s) caused the problem. You may also get more detailed information such as the line number which had the error. In this case you can open the file on the supercomputer and view the line, as the line number given will not match with the line in your working directory on PUMA due to merging source code and the use of include files. Remember to make any required changes to your PUMA source code however!
Reconfiguration Output (.rcf.leave)
This gives output from the reconfiguration step, if run. At older UM versions, such as UM7.3 this output was found in the model output .leave file.
Model Output (.leave)
This gives output from the code which is generated as it is running, although this file is only updated and closed when the job finishes. To view the output generated as it is running you will need to see the output in the pe_output/ directory mentioned above.
To run efficiently the UM is split into many domains, which communicate with each other with parallel calls, during runtime. The exact decomposition is defined in Model Selection → User Information and Submit Method → Job submission method, in the number of processes East-West and North South boxes. If you have a 16x16 decomposition there will be 256 processes, running on 256 cores of the supercomputer (4 nodes of MONSooN,