UKCA Chemistry and Aerosol Tutorials: Python notebooks with Cylc
UKCA Chemistry and Aerosol Tutorials at UMvn13.9
| Difficulty | EASY |
| Time to Complete | Under 1 hour |
| Video instructions | https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aysibeNdLUY |
During these Tutorials several Jupyter notebooks are provided using both cf-python and the Iris Python libraries. On pre-installed virtual machines these can be found in the
Tutorials/UMvn13.9/notebooks
Due to the SSH connection you will be making to these virtual machines, it is better to run jupyter remotely and then connect to it from the browser on your desktop machine.
Copies of these notebooks have also been made available on GitHub.
These notebooks can be run after starting the Cylc GUI on your VM. This can be done with the command
cylc-gui &
which will open a new lxterminal and run the Cylc GUI command within it. You will need to connect to Cylc from a web browser on your own laptop.
How to connect
- On your VM run the command cylc-gui & to start the Cylc GUI server
- On your personal computer, open a connection to your AWS instance using one of the methods below.
- On your desktop machine, connect to the following web address using a web browser (Firefox recommended):
- You may need to enter the password UKCATraining to complete the connection
- Once you have connected to Cylc, on Jupyter Lab which will open a new Jupyter lab instance in a new tab
- When running your notebooks, be sure to use the ukca kernel, selectable from the top right of each notebook
Note that if you try to connect to the link on your personal computer before running cylc-gui on the VM you will have an error in your browser, even if you have connected properly.
Technical notes
The above instructions make use of some alias and shortcuts to work. The full details of this are:
On your personal computer
Windows via MobaXTerm
On Windows you can use MobaXTerm to connect to the AWS instance to tunnel through to allow you to run Jupyter remotely.
Graphical method
You can use the MobaSSHTunnel (port forwarding) tool to set this up. First, go to the Tools menu and select MobaSSHTunnel (port forwarding)
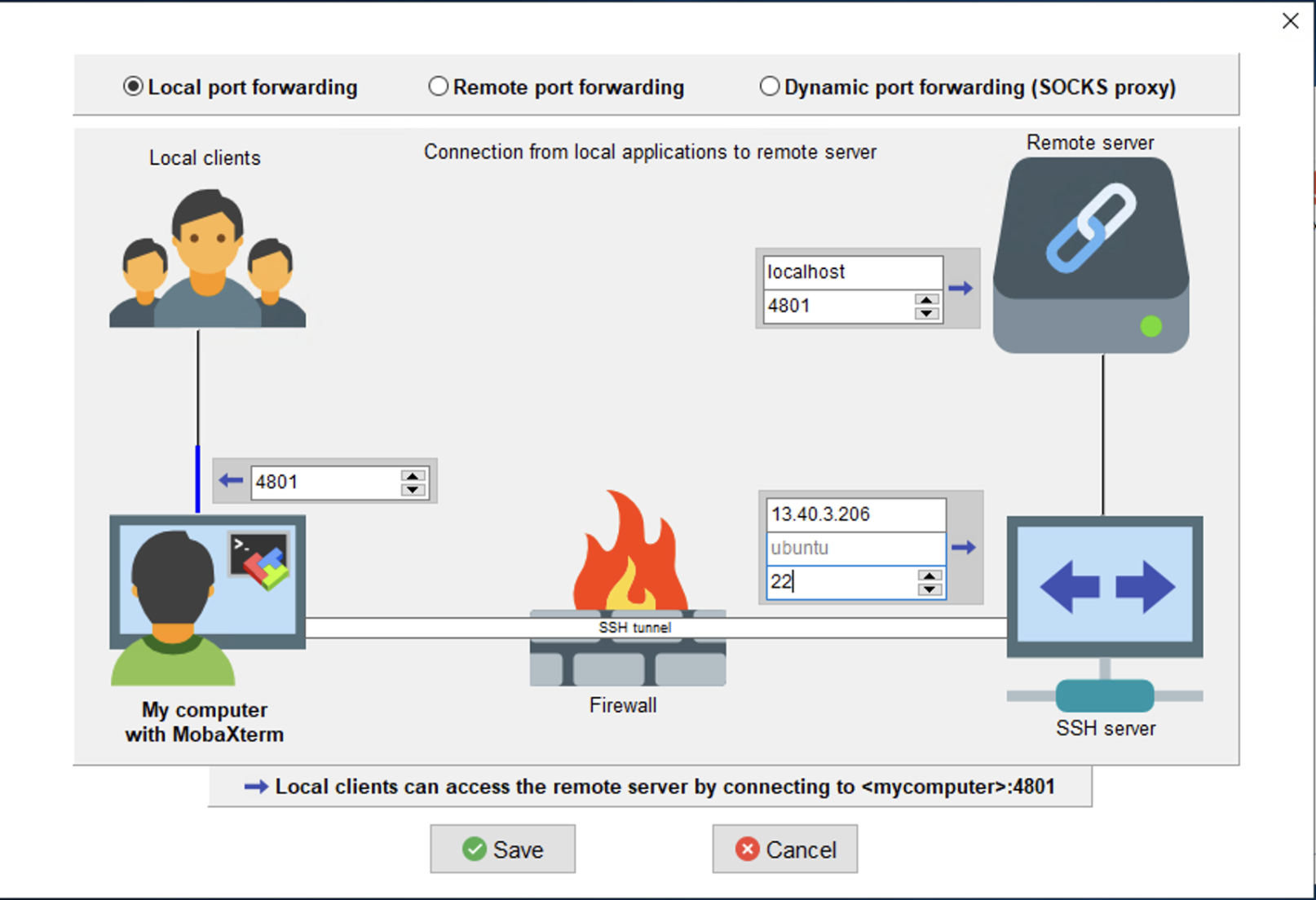
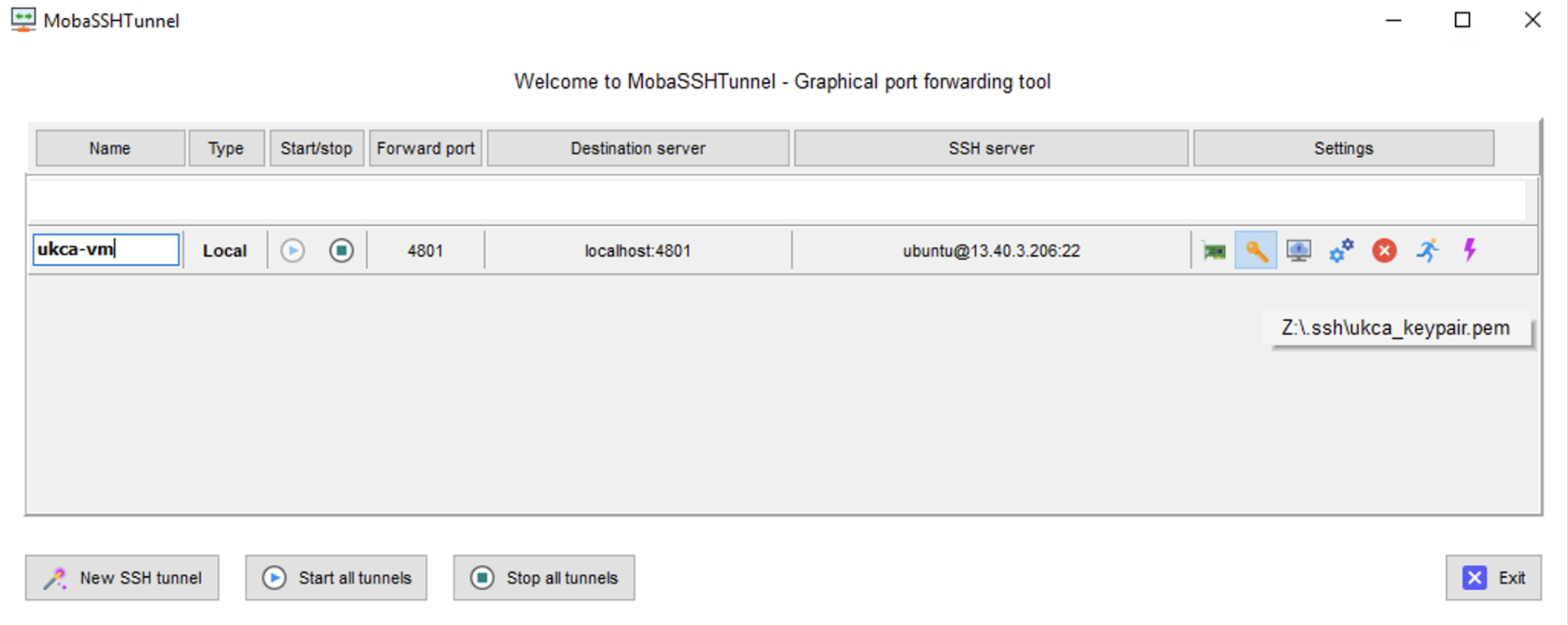
then click New SSH tunnel in the bottom left corner. Then you will need to set the following information, changing the <SSH server> information to the IP address of your training virtual machine
and then select your SSH key by clicking the key symbol, navigating to it using the file browser menu that will open, and selecting it
Once you have done this you can start and stop the tunnel by clicking the play (triangle) and stop (square) buttons.
| Option | Setting |
|---|---|
| <Forwarded port> | 4801 |
| <SSH server> | [EC2 VM IP ADDRESS] (e.g. 13.40.3.206) |
| <SSH login> | ubuntu |
| <SSH port> | 22 |
| <Remote server> | localhost |
| <Remote port> | 4801 |
| Set SSH key file via key icon on entry in main MobaSSHTunnel panel | The path to your [KEY NAME] key file (navigate via file manager) |
Terminal method
You could also do this by opening a local session, where you run the following command, e.g.
ssh -N -f -L localhost:4801:localhost:4801 -i /drives/x/path/to/[KEY NAME] ubuntu@[EC2 VM IP ADDRESS]
Where /drives/x/path/to/[KEY NAME] is the full path to the location of your private key file that you use to connect to the AWS instance and x is the drive letter, e.g. c for your C: drive.
Once this connection has been established you will be able to connect using the link above. To close this connection, you will need to shut down MobaXTerm.
SSH via a terminal (macOS or GNU/Linux)
You will be able to connect using the following SSH command:
ssh -N -f -L localhost:4801:localhost:4801 -i /path/to/[KEY NAME] ubuntu@[EC2 VM IP ADDRESS]
This connection can be killed using
lsof -ti:4801 | xargs kill -9
You could also edit your ~/.ssh/config file to include the following
Host ukca
Hostname [EC2 VM IP ADDRESS]
User ubuntu
IdentityFile /path/to/[KEY NAME]
HostKeyAlgorithms ssh-rsa
Host cylc-gui
Hostname [EC2 VM IP ADDRESS]
User ubuntu
ControlMaster auto
ControlPath ~/.ssh/control_sockets%r@%h:%p
IdentityFile /path/to/[KEY NAME]
HostKeyAlgorithms ssh-rsa
and then connect for normal work usage by
ssh -X ukca
and connect to use Jupyer by
ssh -N -f -L localhost:4801:localhost:4801 cylc-gui
You could also make an alias in your ~/.zshrc or ~/.bashrc, e.g.
alias cylc-gui='ssh -N -f -L localhost:4801:localhost:4801 cylc-gui'
and then use the command cylc-gui from within your terminal.
Once the connection has been established you'll be able to connect using the link above.
To close the connection, type
ssh -O exit -N -f -L localhost:4801:localhost:4801 cylc-gui
On the virtual machine
You will not need to make any changes on the virtual machine - this section is for information only.
The following alias is set in the ~/.bashrc file on the VM:
alias cylc-gui='lxterminal -l -e '\''cd && cylc gui --ServerApp.open_browser=False --ServerApp.port=4801 --ServerApp.ip=0.0.0.0 --IdentityProvider.token=UKCATraining'\'''
This means that when you run the command cylc-gui you then launch a new terminal running the Cylc GUI. From within this GUI you can then launch Jupyter lab in a new browser tab.
If you have having issues connecting to the Jupyter server over SSH in your local browser and you are connecting via [UKCA_Chemistry_and_Aerosol_Tutorials:_Configuring_X2Go_for_AWS X2Go] then it is possible to open a local Cylc GUI instance using the Firefox browser installed on the VM. However, it will not be very responsive and might be quite laggy resulting in a poor user experience. It is not recommended to try to open Jupyer in the VM's browser over an SSH connection, as the performance will be even worse.
The following has also been set, although it is usually only needed for Vagrant boxes that use VirtualBox
c.NotebookApp.ip = '0.0.0.0'
Python environment
A new kernel for use by Jupyter lab has been installed on the VM to use. This has been configured using ipykernal as described here and using this environment.
To be able to use this environment within a terminal, you will first need to run the following command to get the conda command
. "/opt/deployment/miniforge/etc/profile.d/conda.sh"
and then activate the environment
conda activate ukca
However, be careful not to run any Rose or Cylc commands when using this environment, as the python install here may clash. To deactivate this environment using
conda deactivate
UKCA Chemistry and Aerosol Tutorials at UMvn13.9
Written by Luke Abraham 2025.