Difference between pages "Direct effect from GLOMAP-mode aerosol to the Edwards-Slingo radiation scheme" and "ARCHER porting"
From UKCA
(Difference between pages)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | Several of the [[UKCA Release Jobs]] have been ported from HECToR to ARCHER, and their [[UKCA_Release_Jobs#Job_List|jobids]] are detailed on that page. |
||
| − | The UKCA model is configured into the HadGEM3 climate model |
||
| − | with an interface to the Edwards-Slingo radiation scheme |
||
| − | to allow the direct radiative effects of the GLOMAP-mode |
||
| − | aerosol to feedback on the model circulation. |
||
| − | A double-call method is used in this "RADAER" interface |
||
| − | to allow the direct radiative forcing to be diagnosed |
||
| − | and stored in the model output files. |
||
| + | ==Timings== |
||
| − | For the existing CLASSIC aerosol scheme used |
||
| − | in HadGEM2-ES and previous HadGEM versions, |
||
| − | the aerosol is considered as an external |
||
| − | mixture of different aerosol types (sulphate, |
||
| − | biomass, soot, biogenic and sea-salt). |
||
| − | Then, for the direct aerosol forcing, the optical properties |
||
| − | from each of these types was considered separately. |
||
| − | The interface to the Edwards-Slingo radiation scheme used |
||
| − | in HadGEM is based on look-up tables (from Mie calculations) |
||
| − | for the optical properties of each particle type |
||
| − | as a function of relative humidity. |
||
| + | [[File:CCMI_timings_ARCHER.png|300px|thumb|right|Scaling and efficiency profiling for N48L60 UKCa CheS+ on ARCHER]] |
||
| − | In contrast to CLASSIC, GLOMAP-mode assumes each mode |
||
| − | consists of an internal mixture of the different aerosol |
||
| − | components (e.g. sulphate, black carbon and organic carbon). |
||
| − | The water content is evaluated within this assumption using |
||
| − | the ZSR algorithm (Stokes and Robinson, 1966), using water activity data from Jacobson et al. (1996). |
||
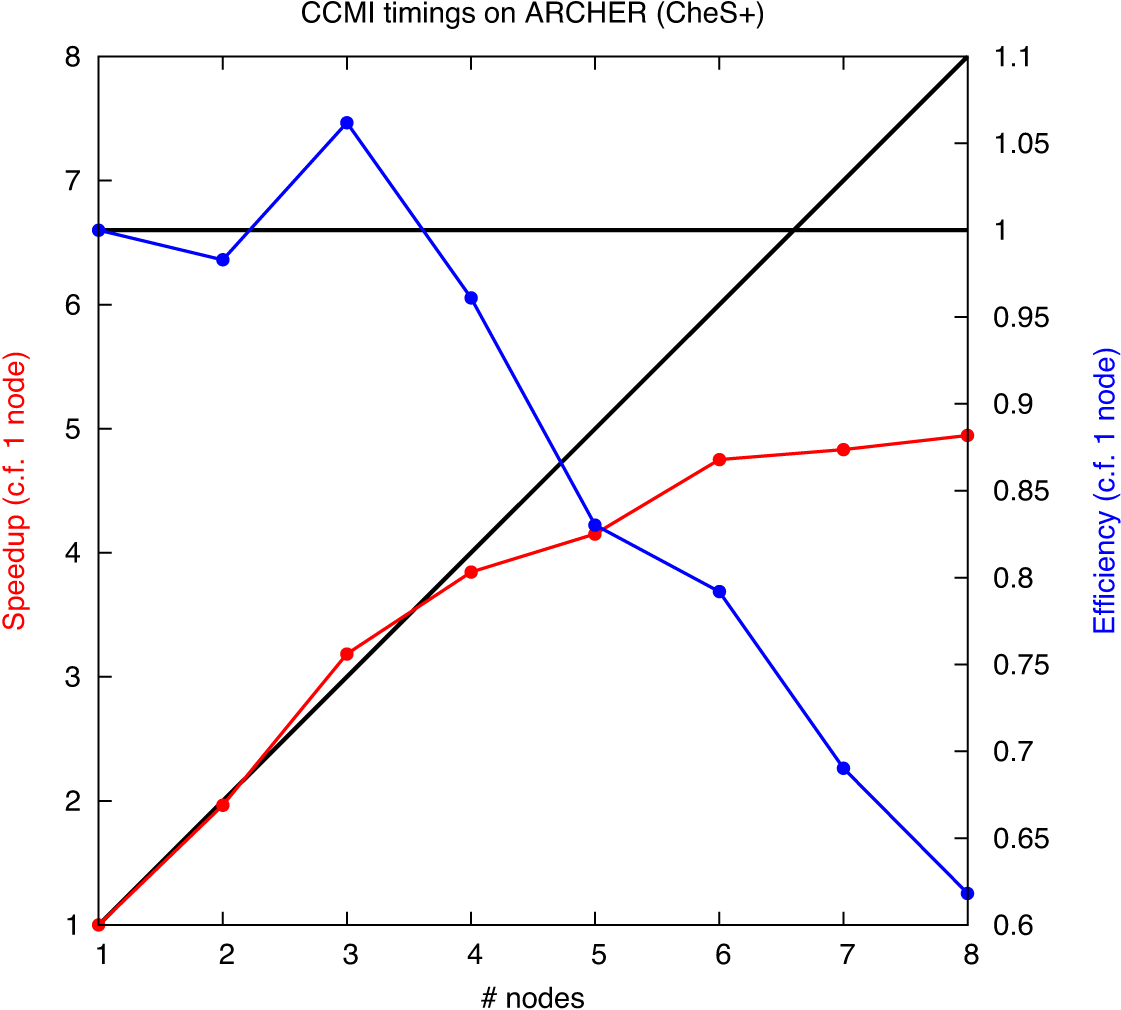
| + | The plot shows how UKCA scales when ported to ARCHER. The most efficient number of nodes to use is 3 (8x9), although the model will run fastest on 6 nodes (e.g. 16x9 or 12x12). Moving to 3 nodes from 6 will increase the run-time by 50%. |
||
| − | Whereas the look-up tables for the CLASSIC aerosol scheme were |
||
| − | based only on relative humidity and wavelength; for GLOMAP-mode, the |
||
| − | information on mean particle radius and composition for each |
||
| − | of the internally-mixed size modes is used. A volume-average |
||
| − | mixing rule is used over the components present (including water) |
||
| − | to calculate the real and imaginary parts of the refractive |
||
| − | index. The particle size determines the Mie parameter in |
||
| − | relation to the wavelength. The look-up tables have been |
||
| − | calculated based on the integrals across each of the |
||
| − | spectral bands for the short-wave and long-wave used by HadGEM. |
||
| + | ==Code Changes== |
||
| − | References: |
||
| + | ===Cray cce Fortran Compiler=== |
||
| − | Bellouin, N., 2011, |
||
| − | Interaction of UKCA aerosols with radiation: UKCA RADAER |
||
| − | Met Office Hadley Centre Internal Report [[File:UKCA_RADAER.pdf]]. |
||
| + | Corrections required for the Cray cce compiler on archer can be found on the [[Bugfixes#Cray_compiler_on_ARCHER|bugfixes page]]. |
||
| − | Jacobson, M. Z., Tabazadeh A. and Turco, R. P., |
||
| − | Simulating equilibrium within aerosols and nonequilibrium between gases and aerosols, |
||
| − | J. Geophys. Res., 101, pp. 9079-9091, 1996. |
||
| − | |||
| − | Stokes, R.H. and Robinson, R.A., Interactions in aqueous non-electrolyte solutions: I. Solute-solvent equilibria. |
||
| − | J. Phys. Chem., 70, pp. 2126-2130, 1966. |
||
| − | |||
| − | For more details about the interface to the Edwards-Slingo |
||
| − | radiation scheme and the calculations of the optical properties |
||
| − | of the aerosol, please contact Nicolas Bellouin (UK Met Office) |
||
| − | nicolas.bellouin@metoffice.gov.uk. |
||
Revision as of 17:12, 14 January 2014
Several of the UKCA Release Jobs have been ported from HECToR to ARCHER, and their jobids are detailed on that page.
Timings
The plot shows how UKCA scales when ported to ARCHER. The most efficient number of nodes to use is 3 (8x9), although the model will run fastest on 6 nodes (e.g. 16x9 or 12x12). Moving to 3 nodes from 6 will increase the run-time by 50%.
Code Changes
Cray cce Fortran Compiler
Corrections required for the Cray cce compiler on archer can be found on the bugfixes page.